| Basic Information | |
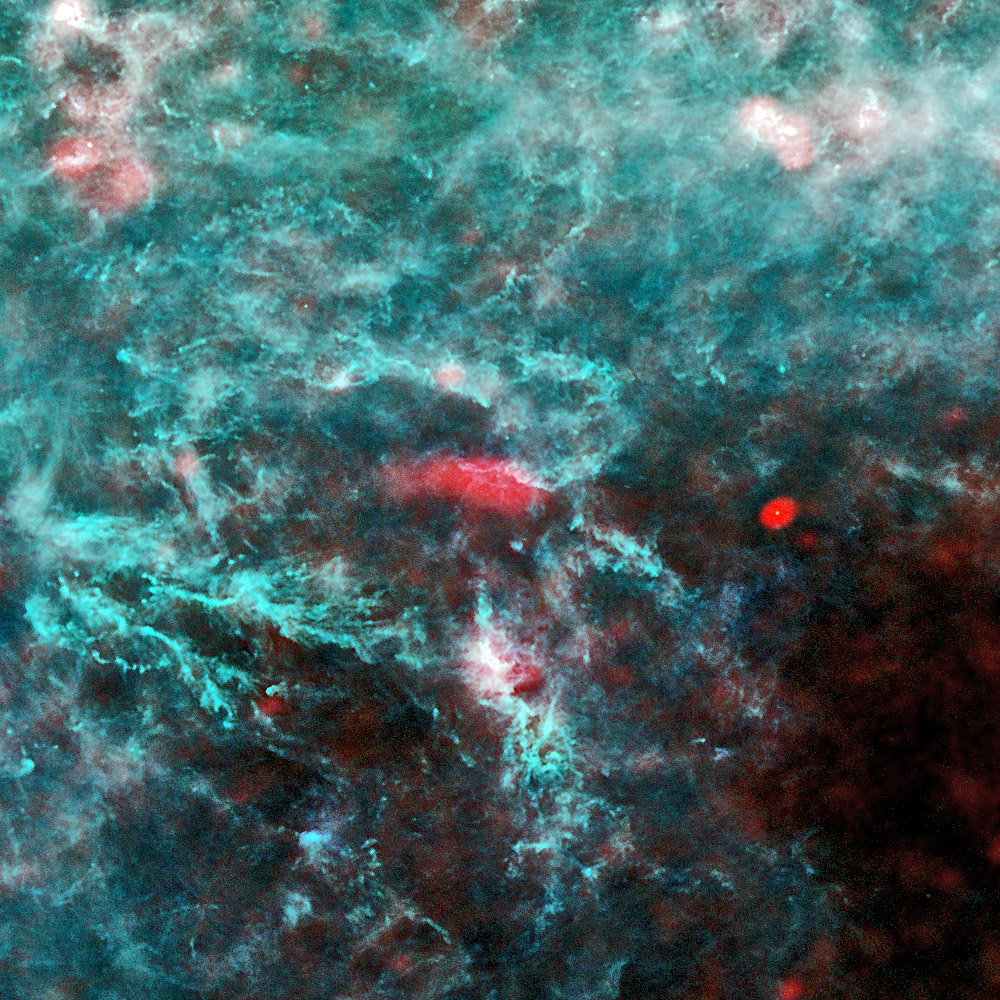
| What is this? | The sky around the constellation of Perseus, centred on the Californai Nebula |
| Where is it in the sky? | in the Constellation of Perseus the Hero |
| How big is it? | The image is about 30 degrees across |
| How far away is it? | The California Nebula in the centre is about 1500 light years away |
| What do the colours represent? | Red colours show gas and electrons, and while the green and blue colours show dust |
Downloads
The region of the sky around the constellation of Perseus, as seen by Planck at microwave wavelengths. The red colour shows longer wavelength light which is emitted by gas and electrons, while the green and blue material is emitted by dust laced between the stars. The gas and dust are what stars are made of, and measuring their distribution is crucial to working out how stars form, and what effect the properties of the gas and dust can have on the resulting stars. The red feature in the centre is the California Nebula, a cloud of gas which is reflecting the light from a nearby star.

Visible only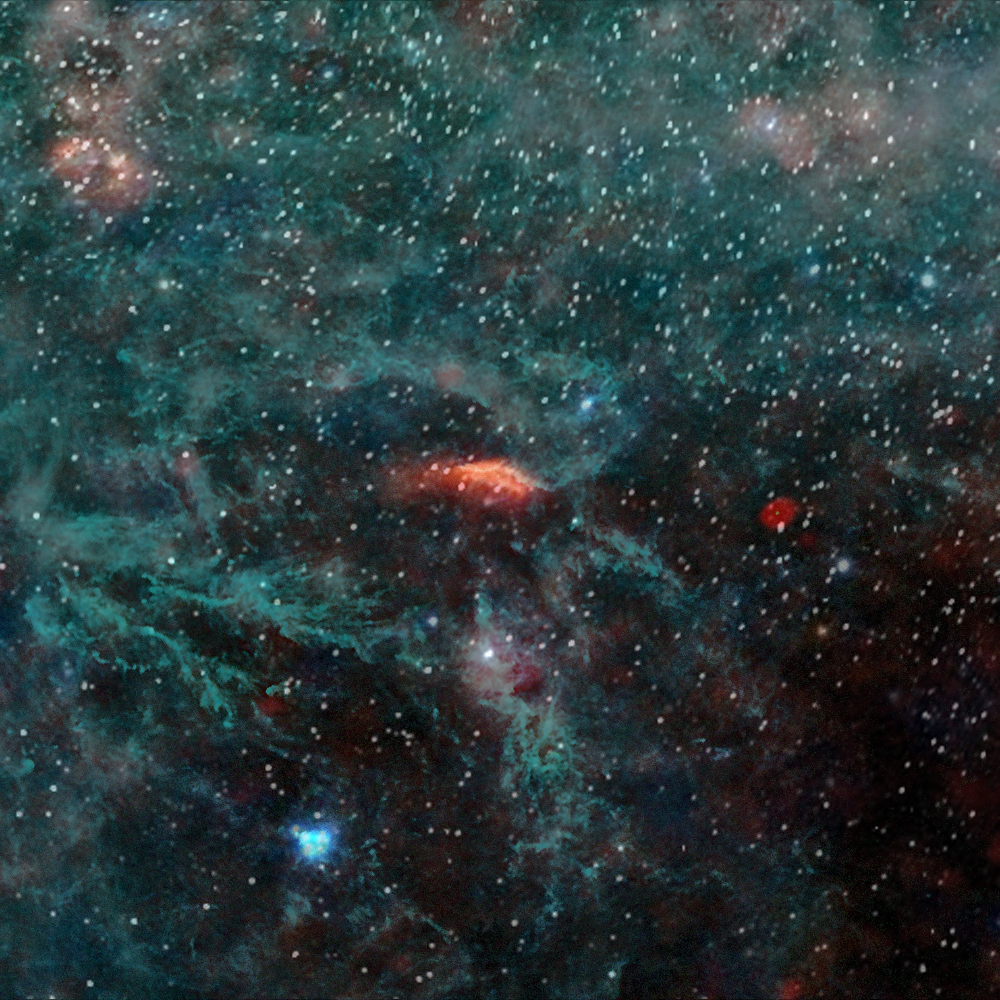 
Visible + Planck
The same patch of sky is shown on the right at visible wavelengths, with the Planck image overlaid if you hover your mouse over it. The cluster of stars in the bottom left is the Pleiades, or Seven Sisters, which are far less prominent at microwave wavelengths. The feature near the top left is NGC 1893, a nebula housing a cluster of stars, actually in the nearby constellation of Auriga. To the right of the centre, Planck sees a bright red object, which is a galaxy known as “Perseus A” or NGC 1275. It marks the centre of the Perseus galaxy cluster, and due to its very active nature emits lots of radio and x-ray emission.
Because Planck is mapping the entire sky, it can observe the gas and dust over the whole sky. Other experiments, such as Herschel, can examine the dust at much higher resolution, but only over small regions.
You can also see a similar image of a region of sky in the constellation of Orion here.
You can also see this part of the sky at different wavelengths on Chromoscope.